Pets, just like humans, can experience anxiety. Whether it’s separation anxiety, fear of loud noises, or stress from a new environment, anxiety can affect their behavior and well-being. At PetFriends, we believe understanding pet anxiety is key to providing the best care and comfort to your beloved companion.
What Is Pet Anxiety?
Pet anxiety is a state of nervousness, fear, or stress that pets experience in response to certain triggers. It can manifest as restlessness, excessive barking or meowing, destructive behavior, or even health problems.
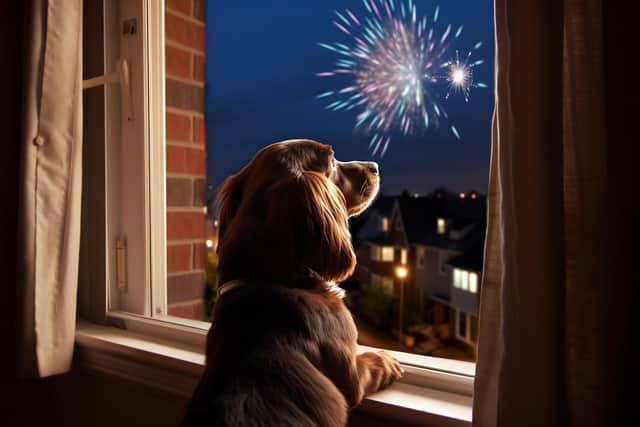

Common Signs of Anxiety in Pets
- Pacing or restlessness
- Excessive vocalization (barking, whining, meowing)
- Destructive chewing or scratching
- Hiding or avoidance
- Excessive licking or grooming
- Loss of appetite
- Trembling or shaking
- Accidents inside the house despite training
Common Causes of Anxiety in Pets
- Separation from owners: Many pets feel stressed when left alone.
- Loud noises: Thunderstorms, fireworks, or construction sounds can trigger fear.
- Changes in environment: Moving to a new home, new family members, or changes in routine.
- Past trauma: Rescue pets may have experienced neglect or abuse.
- Lack of socialization: Pets not exposed to different people or situations may become fearful.

How to Help a Pet with Anxiety
1. Create a Safe Space
Provide a quiet, comfortable area where your pet can retreat when feeling overwhelmed. A cozy bed, crate, or a familiar room works well.
2. Maintain a Consistent Routine
Predictability helps reduce stress. Stick to regular feeding, walking, and playtimes.
3. Exercise and Mental Stimulation
Physical activity helps burn excess energy and release calming endorphins. Puzzle toys and training sessions also provide mental engagement.
4. Use Comforting Aids
Products like anxiety wraps, calming collars, or pheromone diffusers can ease stress.
5. Avoid Punishment
Never punish anxious behavior; this can worsen fear and stress.
6. Gradual Desensitization
Slowly expose your pet to triggers in a controlled way, rewarding calm behavior.
7. Consult Your Veterinarian
In severe cases, professional guidance and medication may be necessary.
When to Seek Professional Help
If your pet’s anxiety leads to self-harm, aggression, or severe distress, consult a veterinarian or a certified animal behaviorist. Early intervention improves outcomes.

Final Thoughts
Understanding and managing pet anxiety improves your pet’s quality of life and strengthens your bond. With patience, love, and the right strategies, you can help your furry friend feel safe and happy.
At PetFriends, we’re here to support you and your pet every step of the way.